•
2min
Model for Local and Non-Linear Time and Space
Authors:
Martin AlpertProfile:
Martin Alpert
Categories:
Entropy
Abstract
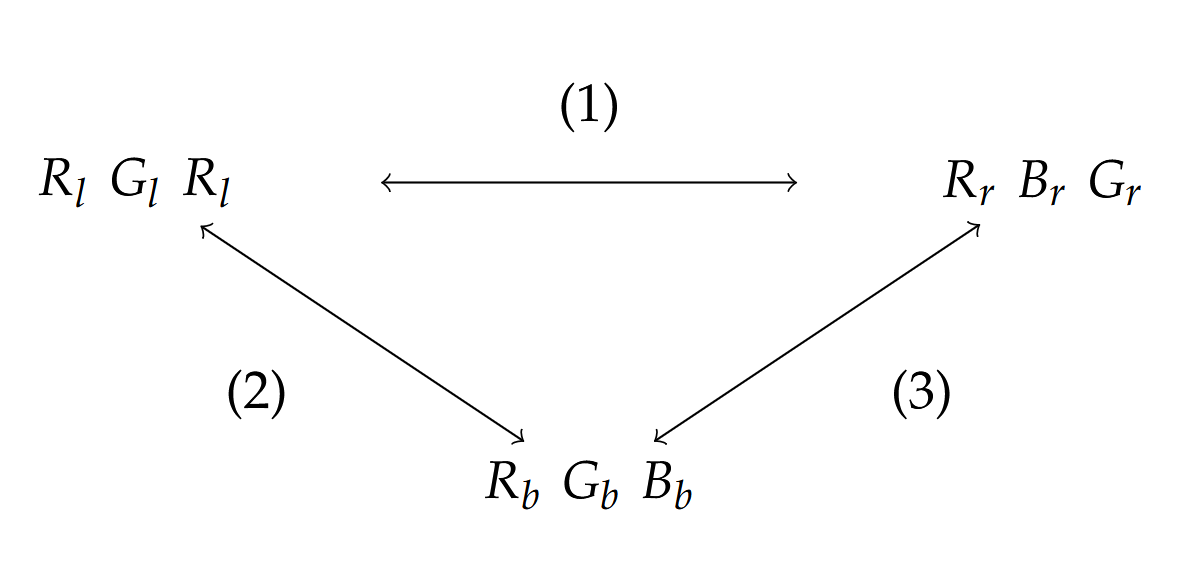
In this theory, duration is differentiated from time and length is differentiated from space. 1 This theory proposes that space is generated by relationships which is quantified by entropy at each 2 present time and time is quantitatively related to entropy changes. That is, relationships are the 3 basis of each configuration which result in space and changes between relationships results in time. 4 One example is Bell’s inequality violation where an interpretation of observations is that it confirms 5 the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics so properties only exist when observed. In 6 contrast, this theory proposes that the same results are obtained for real properties in nonlinear 7 local time and space. Hidden variables are the generated time and space. Physical phenomena 8 are typically described in background spacetime which, per this theory, is a statistical average of a 9 large number of relationships and relationship changes. A consequence of this theory demonstrated 10 in this paper is that superposition in double slit systems and entanglement observations in Bell’s 11 inequality are explained by the same quantum mechanical mechanism. This theory is applied to the 12 twin paradox, mass change with speed, the origins of the Pauli Exclusion Principle, particle decay, 13 deBroglie waves, black holes, inflation post-big bang and how space and time are related to the four 14 forces. Experiments are proposed that could validate this theory.